Overcoming Digital Transformation Challenges | Key Strategies
Discover effective solutions for digital transformation challenges and unlock success. Learn how to conquer common obstacles today!
Why Digital Transformation is Hard
Digital transformation offers immense potential, but it's rarely straightforward. This listicle identifies seven key digital transformation challenges impacting organizations today. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for AI professionals, developers, entrepreneurs, and digital marketers alike. We'll explore common roadblocks like legacy system integration, cultural resistance, and budget constraints, and provide insights to help you navigate these complexities. This list will equip you to better plan and execute your digital transformation initiatives.
1. Legacy System Integration
Legacy system integration is a significant digital transformation challenge that involves connecting older, often outdated, systems with modern digital technologies. These legacy systems, while potentially using obsolete technology like COBOL and lacking modern features like APIs, often hold crucial business data and support vital processes. Replacing them entirely is usually extremely expensive and disruptive, making integration a necessary but often complex undertaking.
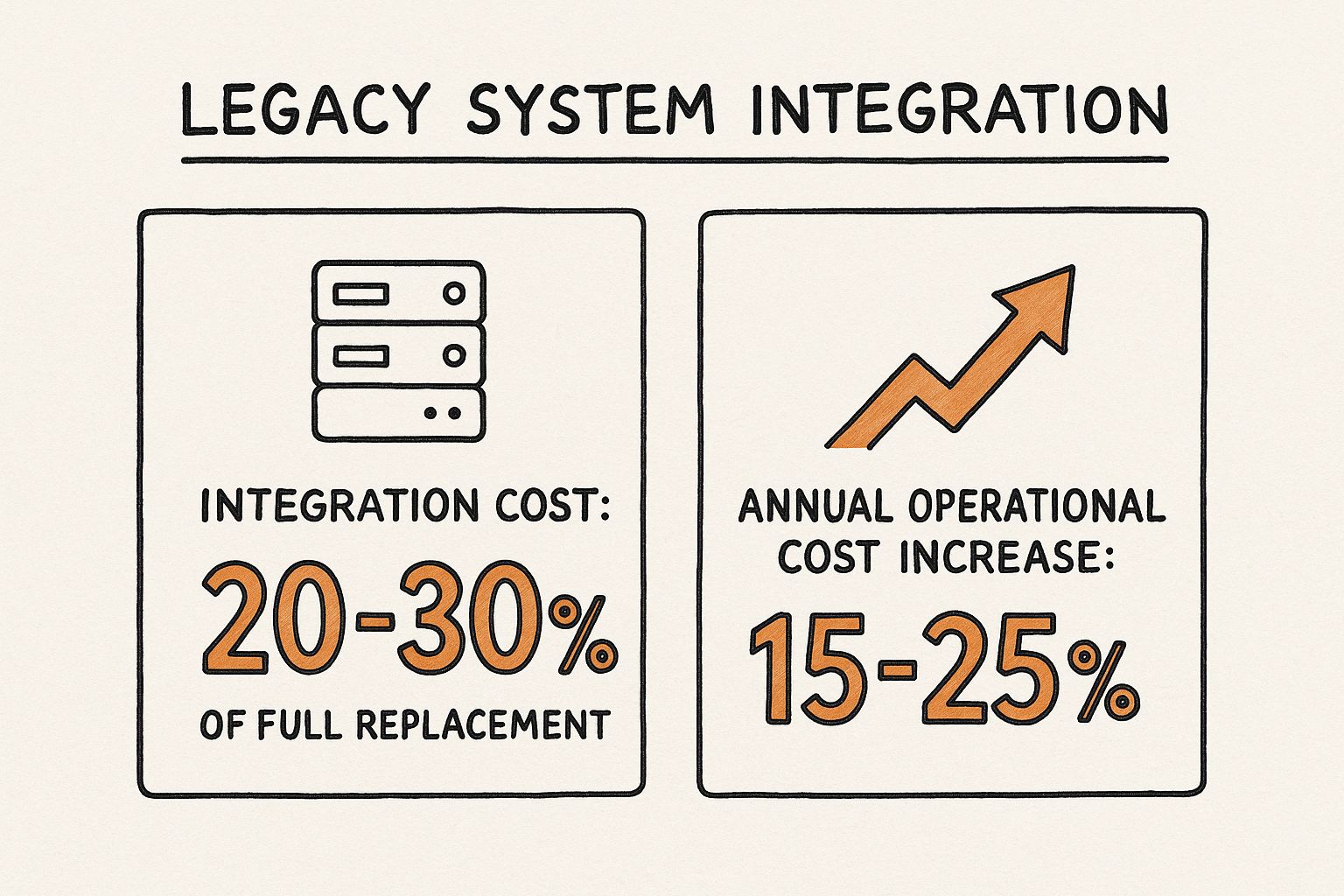
The infographic above visualizes some key statistics around legacy system integration. It highlights that 70% of businesses still rely on legacy systems, indicating how widespread this challenge is. Furthermore, 60% of IT budgets are allocated to maintaining these systems, demonstrating the significant financial burden they represent. The statistic showing that only 30% of companies have successfully modernized their legacy systems underscores the complexity and difficulty of this process. These numbers clearly demonstrate the prevalence of legacy systems, the associated costs, and the challenges in modernizing them, making integration a critical aspect of digital transformation.
This challenge arises due to several factors. Incompatible data formats and structures, lack of API accessibility, outdated programming languages, limited documentation, and performance bottlenecks when connecting with modern systems all contribute to the complexity. However, successful integration allows organizations to preserve valuable historical data, reduce immediate capital expenditure compared to full replacement, adopt a phased approach to digital transformation, and maintain business continuity.
On the other hand, legacy system integration also introduces its own set of drawbacks. It creates technical debt, requiring specialized, and increasingly scarce, legacy skills. It can limit the functionality of newer systems and introduce security vulnerabilities. Moreover, maintaining these integrated systems can lead to higher long-term costs. Learn more about Legacy System Integration
Several high-profile examples showcase both the challenges and rewards of legacy system integration. JP Morgan's integration of its legacy COBOL systems with cloud infrastructure using middleware solutions demonstrates how even large financial institutions grapple with this issue. Maersk, a global shipping giant, implemented API layers to connect mainframe shipping systems with digital customer platforms, highlighting the value of phased integration. ING Bank's gradual modernization strategy involved creating bridges between core banking systems and digital channels, emphasizing the importance of maintaining business continuity during the transition.
So, when should you consider legacy system integration? This approach is vital when a complete system overhaul is too costly or disruptive. It’s particularly relevant for organizations heavily reliant on older systems containing critical data, allowing them to leverage the value of existing investments while gradually transitioning to newer technologies. For AI professionals, software engineers, and tech-savvy entrepreneurs leading digital transformation initiatives, understanding these challenges is crucial.
To navigate this complex process, consider these actionable tips:
- Implement middleware or integration platforms (ESB, iPaaS): These tools act as a bridge between legacy and modern systems, facilitating data exchange and communication.
- Create API wrappers around legacy functionality: This approach exposes legacy system capabilities to modern applications through APIs, enhancing interoperability.
- Consider containerization to isolate legacy applications: This helps manage dependencies and improves compatibility with modern infrastructures.
- Document existing system knowledge: Capture the expertise of current system experts before they leave, preserving valuable institutional knowledge.
- Prioritize integration for high-value business processes: Focus initial efforts on integrating systems that support the most critical business functions.
Concepts like Gartner's Bimodal IT approach, which advocates managing two separate but coherent modes of IT delivery – one focused on stability and the other on agility – and offerings like IBM's mainframe modernization services and MuleSoft's integration platform, have further popularized and provided solutions for legacy system integration. This challenge remains a key consideration for anyone navigating the complexities of digital transformation.
Get started with your lifetime license
Enjoy unlimited conversations with MultitaskAI and unlock the full potential of cutting-edge language models—all with a one-time lifetime license.
Demo
Free
Try the full MultitaskAI experience with all features unlocked. Perfect for testing before you buy.
- Full feature access
- All AI model integrations
- Split-screen multitasking
- File uploads and parsing
- Custom agents and prompts
- Data is not saved between sessions
Lifetime License
Most Popular€99€149
One-time purchase for unlimited access, lifetime updates, and complete data control.
- Everything in Free
- Data persistence across sessions
- MultitaskAI Cloud sync
- Cross-device synchronization
- 5 device activations
- Lifetime updates
- Self-hosting option
- Priority support
Loved by users worldwide
See what our community says about their MultitaskAI experience.
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
2. Cultural Resistance to Change
One of the most significant digital transformation challenges is cultural resistance to change. This represents the human dimension of transformation, going beyond the implementation of new technologies and addressing the impact on people. It manifests as a reluctance among employees to adopt new technologies, processes, or ways of working. This resistance can stem from various sources: fear of job displacement due to automation, comfort with established routines, a lack of necessary digital skills to navigate new systems, or previous negative experiences with poorly managed change initiatives. It's often cited as the biggest barrier because technology implementation alone cannot drive transformation; true change requires human adoption and adaptation.

This resistance can manifest in several ways: employee fear and anxiety surrounding new technologies, management hesitancy to disrupt established (even if inefficient) processes, departmental silos fiercely protecting their territory and resisting integration, skepticism arising from previous failed transformation attempts, and generational differences in digital adaptability. For AI professionals, developers, and tech-savvy entrepreneurs, understanding this human element is crucial for successful implementation of any new technology, be it machine learning models, software platforms, or innovative business processes.
While cultural resistance presents a significant hurdle, it’s not entirely negative. Some resistance can be valuable, highlighting legitimate concerns with proposed changes. This critical questioning, if properly addressed, can improve implementation approaches and ultimately lead to a more robust and user-friendly final product. Addressing resistance effectively can also foster stronger organizational buy-in and force leadership to articulate a clear value proposition for the transformation, benefiting everyone involved.
However, the downsides are substantial. Resistance significantly slows the transformation pace, potentially impacting deadlines and budgets. It can create shadow IT environments where employees utilize unsanctioned technologies to circumvent the formal, resisted systems. This creates security risks and data silos, defeating the purpose of the transformation. Moreover, resistance reduces the return on investment (ROI) on technology investments as adoption rates remain low. It also creates morale issues and can even lead to a talent exodus as frustrated employees seek opportunities elsewhere. Finally, it may lead to partial implementations that deliver limited value, failing to achieve the intended transformation goals.
Several prominent examples demonstrate how to overcome cultural resistance. Microsoft's cultural transformation under Satya Nadella shifted the company from a competitive to a collaborative mindset, unlocking innovation. Adobe successfully transitioned from packaged software to subscription services through comprehensive change management, addressing employee and customer concerns. DBS Bank transformed from a traditional bank to a digital leader through cultural programs like 'GANDALF' (Google, Amazon, Netflix, etc.), encouraging employees to learn from leading tech companies.
To navigate this complex challenge, consider these actionable tips:
- Create digital champions within each department: These individuals can advocate for the change and provide peer-to-peer support.
- Implement continuous training and upskilling programs: Address the skills gap and alleviate fears around new technologies.
- Communicate "what's in it for me" clearly to all stakeholders: Highlight the individual benefits of the transformation, not just the organizational ones.
- Start with quick wins to build momentum and trust: Demonstrate early success to reduce skepticism and build confidence.
- Involve resistant employees in the design process: Foster ownership and incorporate their feedback to improve adoption.
- Celebrate and reward early adopters and innovators: Recognize and reinforce positive behaviors.
The importance of addressing cultural resistance is emphasized in established change management frameworks such as John Kotter's 8-Step Change Model, MIT Sloan's research on digital transformation, and McKinsey's organizational health index. These resources offer valuable insights for leaders navigating the human side of digital transformation. By acknowledging and effectively managing cultural resistance, organizations can pave the way for successful and sustainable digital transformation.
3. Data Security and Privacy Compliance
Data security and privacy compliance represent a significant hurdle in any digital transformation journey. As organizations increasingly rely on digital technologies, they collect and process vast amounts of customer data, making robust security measures paramount. This challenge involves safeguarding sensitive information from breaches while simultaneously navigating an increasingly complex web of global privacy regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and others. This is a critical digital transformation challenge because a security breach can damage an organization's reputation, erode customer trust, and lead to hefty financial penalties.
This challenge intensifies as digital transformation initiatives introduce new data collection points, cloud migrations, IoT devices, and third-party integrations. Each of these elements expands the potential attack surface and adds layers to the compliance requirements. Features of this challenge include a constantly evolving regulatory landscape, cross-border data transfer complexities, increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, the need for end-to-end data encryption, balancing security with user experience, and managing consent and data subject rights.
Cybersecurity is a critical aspect of digital transformation, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Implementing robust security measures is crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining customer trust. For SMEs looking to enhance their web security, resources like this guide on how to boost your SME's web security can be invaluable.
Successfully navigating this digital transformation challenge has several advantages. Strong security builds customer trust and enhances brand reputation. Adhering to compliance frameworks provides a structured approach to data governance. Proper implementation significantly reduces the costs associated with breaches and regulatory penalties. Moreover, robust data security and privacy practices can become a competitive advantage if executed effectively.
However, there are also downsides. Implementing and maintaining ongoing compliance can be costly. Security measures may slow down development and deployment cycles. There's also the potential for friction in user experiences, particularly if security measures are perceived as cumbersome. Continuous monitoring, updating, and maintaining consistency across global operations present ongoing challenges.
Real-world examples demonstrate the importance of addressing data security and privacy compliance:
- Salesforce's Shield platform: Offers financial services customers robust encryption and compliance monitoring tools.
- Apple: Leverages its privacy-focused approach as a key market differentiator.
- Mastercard: Implements tokenization to secure payment data during its digital transformation.
To effectively manage data security and privacy during digital transformation, consider these actionable tips:
- Privacy by Design: Implement privacy-by-design principles from the very beginning of each project.
- Data Classification: Create data classification frameworks to prioritize security resources effectively.
- Regular Assessments: Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Deploy DLP systems across the organization to prevent sensitive data from leaving the network.
- Data Retention and Deletion: Establish clear data retention and deletion policies.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Implement strong IAM controls to restrict access to sensitive data.
- Employee Training: Train employees regularly on security best practices.
The importance of data privacy has been popularized by several key developments, including the EU's GDPR implementation in 2018, Ann Cavoukian's Privacy by Design framework, and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. Learn more about Data Security and Privacy Compliance for a deeper dive into best practices. Addressing data security and privacy compliance head-on is not merely a best practice; it's a necessity for any organization undertaking digital transformation. By proactively managing these challenges, organizations can protect their valuable data, maintain customer trust, and unlock the full potential of their digital initiatives.
4. Skill Gaps and Talent Shortages: A Major Digital Transformation Challenge
One of the most significant digital transformation challenges organizations face is the widening chasm between the required digital skills and the available talent pool. This skill gap is a critical bottleneck, often slowing or even derailing transformation initiatives. Simply put, businesses need specialized technical expertise to execute their digital strategies, but these skills are in high demand and short supply. This makes finding, attracting, and retaining top digital talent a constant struggle.
This challenge isn't merely about finding enough bodies to fill seats. It's about securing individuals with highly specialized skill sets in areas like cloud architecture, data science, cybersecurity, AI/ML engineering, and digital product development. The rapid evolution of these technologies further complicates the issue, necessitating continuous learning and adaptation for both existing employees and new hires. This fast-paced change contributes to rapid skill obsolescence, requiring constant investment in upskilling and reskilling.
Features of the Talent Gap Challenge:
- Acute shortage of specialized technical roles: Demand significantly outstrips supply for roles requiring expertise in cutting-edge technologies.
- Competitive recruitment landscape: Organizations compete with tech giants and well-funded startups for a limited pool of talent, driving up salaries and recruitment costs.
- Rapidly changing skill requirements: The constant emergence of new technologies demands continuous learning and adaptation, making it difficult for individuals and organizations to keep pace.
- Geographic concentration of tech talent: Tech hubs like Silicon Valley and Seattle attract a disproportionate share of talent, leaving other regions struggling to find qualified candidates.
- Growing salary expectations for digital roles: The high demand and limited supply of skilled professionals translate into escalating salary expectations, increasing the financial burden on organizations.
- Need for both technical and business understanding: Successful digital transformation requires individuals who not only possess deep technical skills but also understand the business context and can align technology solutions with business objectives.
Pros of Investing in Talent Development:
- Builds long-term capabilities: Upskilling and reskilling create a sustainable talent pipeline and strengthen the organization's internal expertise.
- Improves employee retention and satisfaction: Investing in employee development demonstrates commitment and provides opportunities for career growth, boosting morale and retention rates.
- Drives innovation: A diverse and highly skilled workforce is better equipped to develop innovative solutions and drive digital transformation forward.
- Develops customized skills for specific needs: Training programs can be tailored to address the specific skill gaps within the organization, ensuring relevance and maximizing impact.
Cons of Addressing the Talent Gap:
- High recruitment costs and salary premiums: Attracting top talent in a competitive market requires significant investment in recruitment efforts and competitive salaries.
- Extended time-to-fill for critical positions: Finding the right candidates for highly specialized roles can be a lengthy process, delaying project timelines and hindering transformation efforts.
- Knowledge concentration risks when specialists leave: When key personnel depart, they take valuable knowledge and expertise with them, potentially disrupting projects and creating setbacks.
- Training investments may benefit competitors if retention fails: If employees leave after receiving training, the organization's investment may benefit competitors who hire them.
- Rapid skill obsolescence requires continuous investment: The rapid pace of technological change necessitates ongoing investment in training and development to keep skills current.
Examples of Successful Implementations:
- AT&T's Future Ready initiative: Retraining over 100,000 employees for digital roles demonstrates a large-scale commitment to upskilling and internal mobility.
- Google's apprenticeship programs: Creating alternative talent pipelines by providing training and development opportunities for individuals from non-traditional backgrounds.
- PwC's $3 billion investment in upskilling all 275,000 employees: A significant financial commitment to ensuring that the entire workforce is equipped for the digital age.
Actionable Tips for Addressing Skill Gaps:
- Create internal digital academies for continuous learning.
- Implement mentorship programs pairing digital natives with experienced staff.
- Partner with universities and coding bootcamps for talent pipelines.
- Consider distributed teams to access global talent pools.
- Build clear career paths for digital specialties.
- Use skill-based project staffing to accelerate learning.
- Consider acqui-hiring (acquiring companies for their talent).
Why this challenge deserves its place on the list: The talent gap is a fundamental roadblock to digital transformation. Without the right people with the right skills, organizations simply cannot execute their digital strategies effectively. Addressing this challenge requires a proactive and multifaceted approach that encompasses recruitment, training, retention, and strategic partnerships. The insights and recommendations provided above can help organizations navigate this complex landscape and build a future-ready workforce. This challenge is frequently highlighted by organizations like the World Economic Forum (Future of Jobs reports) and LinkedIn (annual skills gap analyses), and addressed through enterprise training programs offered by platforms like Coursera and Udacity.
No spam, no nonsense. Pinky promise.
5. Budget Constraints and ROI Justification
Digital transformation is no small feat. One of the most significant digital transformation challenges organizations face is securing the necessary budget and justifying the return on investment (ROI). This challenge deserves its place on the list because, without a well-defined financial strategy, even the most promising transformation initiatives can falter. Digital transformation initiatives often require substantial upfront investment in new technologies, infrastructure, talent, and training. However, the returns on these investments can take years to fully materialize, making it difficult to compete with pressing operational needs for limited funds.
This challenge is amplified by the difficulty in quantifying the ROI of transformational projects. While traditional metrics easily capture cost reductions or increased sales, the value derived from a better customer experience, improved operational agility, or enhanced market positioning can be harder to measure. This often leads to under-resourced initiatives or the premature scaling back of crucial transformation efforts due to financial pressure.
Several factors contribute to this budget and ROI challenge: high upfront costs with delayed returns, the inherent difficulty of quantifying intangible benefits, intense competition for resources with immediate business needs, and the frequent occurrence of unexpected costs during implementation. Traditional capital allocation models, often designed for shorter-term returns, can further disadvantage long-term transformation initiatives. Finally, there's often immense pressure for quick wins, which can undermine the focus on long-term, strategic reinvention.
Features of this Challenge:
- High upfront costs with delayed returns
- Difficulty quantifying intangible benefits
- Competition for resources with immediate business needs
- Unexpected costs during implementation
- Traditional capital allocation models that disadvantage transformation
- Pressure for quick wins versus long-term reinvention
Pros of Navigating Budget Constraints:
- Financial constraints can drive prioritization and a sharper focus on value creation.
- ROI discipline helps eliminate low-value initiatives.
- Phased funding approaches reduce overall risk and allow for adjustments based on learnings.
- Budget limitations can encourage creative solutions and strategic partnerships.
Cons of Poorly Managed Budgets:
- Underfunded initiatives often fail to achieve their objectives, leading to wasted resources.
- A short-term financial focus can undermine long-term strategic positioning and competitive advantage.
- Competitors with deeper pockets and a longer-term vision may gain significant market share.
- Stop-start funding creates inefficiencies, disrupts project momentum, and negatively impacts team morale.
- Technical debt can accumulate when corners are cut to meet budget constraints, creating future problems.
Examples of Successful Budget Management for Digital Transformation:
- Target: After initial failures in e-commerce, Target adopted a sequential funding model, allocating resources in stages based on the success of previous phases.
- Domino's Pizza: Their gradual digital investment strategy transformed them from a pizza company into a tech company that sells pizza, demonstrating the power of sustained, strategic investment.
- Capital One: The company implemented an internal venture capital model for FinTech investments, fostering innovation and agility within a larger organization.
Actionable Tips for Overcoming Budget and ROI Challenges:
- Break large initiatives into smaller, measurable projects: This allows for demonstrating value incrementally and securing further funding based on tangible results.
- Develop comprehensive business cases that include non-financial benefits: Articulating the value of improved customer experience or increased agility strengthens the argument for investment.
- Consider alternative funding models like internal venture funding: This approach allows for dedicated funding streams for innovation and transformation.
- Implement value realization tracking from project inception: Continuous monitoring of key metrics helps demonstrate the impact of the transformation.
- Start with high-ROI pilots to build momentum and secure additional funding: Early successes can justify further investment and demonstrate the viability of the overall strategy.
- Partner with vendors offering consumption-based pricing: This can reduce upfront costs and align spending with actual usage.
- Create dedicated transformation budgets separate from departmental allocations: This protects transformation funding from competing operational needs.
Learn more about Budget Constraints and ROI Justification to effectively manage resources during your digital transformation.
The insights offered by Harvard Business Review's research on digital investment strategies, McKinsey's Digital Quotient assessment framework, and the Lean Startup methodology applied to corporate transformations provide valuable frameworks for navigating these challenges. By adopting these strategies and adapting them to their specific context, organizations can successfully overcome budget constraints and justify the ROI of their digital transformation initiatives.
6. Technology Selection and Architecture Decisions: Navigating the Digital Transformation Maze
Technology selection and architecture decisions are critical components of any digital transformation journey, representing a significant challenge for organizations. This challenge earns its place on the list of digital transformation challenges because it directly impacts the success and sustainability of the entire initiative. With a plethora of options available, choosing the right technologies and designing a robust architecture is essential for achieving desired business outcomes. This process, if mishandled, can easily derail a digital transformation project.
In essence, this stage involves determining which technologies (cloud platforms, software solutions, development tools, etc.) will power the transformation and how these technologies will interact with each other within the organization's IT ecosystem. This includes defining the overall structure, including data flow, system integrations, and security considerations. Making the correct choices lays the foundation for agility, scalability, and long-term success.
The Complexity of Choice:
The sheer proliferation of technology options and vendors creates a complex decision-making landscape. Organizations must carefully consider factors like:
- Balancing Best-of-Breed vs. Integrated Platforms: Choosing specialized, best-in-class solutions for individual needs versus opting for integrated platforms that offer a broader range of functionalities but may involve compromises.
- Managing Technical Debt During Transitions: Migrating from legacy systems to new technologies often introduces technical debt that needs to be addressed strategically to avoid hindering future progress.
- Ensuring Scalability for Future Growth: Selecting technologies that can scale to accommodate future business growth and changing demands is paramount.
- Avoiding Over-Engineering or Under-Engineering: Finding the right balance between building robust, future-proof systems and avoiding unnecessary complexity that adds cost and development time.
- Aligning Technology Choices with Organizational Capabilities: Ensuring the chosen technologies are compatible with the organization's existing technical skills and infrastructure.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Enhanced Business Agility: Well-designed architecture enables organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer demands.
- Competitive Advantages: Strategic technology selection can create unique capabilities that differentiate an organization from its competitors.
- Incremental Improvements: Modular approaches allow for phased implementation and continuous improvement.
- Scalability and Cost Efficiency: Cloud technologies offer on-demand scalability and reduced capital expenses.
Cons:
- Long-Term Commitments: Technology decisions create long-term dependencies and commitments.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating multiple vendors and technologies can be complex and costly.
- Adoption Risks: Emerging technologies carry inherent risks associated with early adoption.
- Vendor Lock-in: Dependence on a single vendor can limit future flexibility and negotiating power.
- Capability Gaps: The chosen technology's complexity may exceed the organization's internal technical capabilities.
Success Stories:
- Netflix: Their microservices architecture enables continuous deployment and seamless scaling to handle massive traffic fluctuations.
- LEGO: Their phased cloud migration strategy allows them to balance legacy systems with new capabilities, minimizing disruption.
- Capital One: Their API-first architecture has facilitated participation in the broader fintech ecosystem, fostering innovation and partnerships.
Actionable Tips for Navigating the Technology Landscape:
- Implement a Technology Radar: Use approaches like the ThoughtWorks Technology Radar to systematically evaluate emerging technologies and their potential impact.
- Create Reference Architectures: Develop standardized architectures for consistent decision-making across projects.
- Prioritize Interoperability: Emphasize open standards and APIs to facilitate seamless integration between systems.
- Build Proof-of-Concepts: Test and validate technology choices with small-scale proof-of-concepts before making large investments.
- Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate costs beyond initial implementation, including maintenance, upgrades, and training.
- Design for Change: Adopt modular architectures that allow for flexibility and adaptation to future needs.
- Collaboration is Key: Involve both technical and business stakeholders in key technology and architecture decisions to ensure alignment with business objectives.
Popular Frameworks and Resources:
- ThoughtWorks Technology Radar: Provides insights into emerging technologies and their potential impact.
- Gartner's Hype Cycle: Helps understand the maturity and adoption lifecycle of different technologies.
- AWS Well-Architected Framework: Offers guidance on building secure, resilient, and efficient cloud architectures.
- The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF): Provides a comprehensive enterprise architecture methodology.
By carefully considering these factors and following the tips outlined above, organizations can navigate the complex technology landscape and make informed decisions that drive successful digital transformation initiatives. Addressing this crucial challenge head-on is the key to building a robust, scalable, and future-proof digital foundation.
7. Customer Experience and Journey Integration
One of the most significant digital transformation challenges is Customer Experience and Journey Integration. Digital transformation initiatives often prioritize implementing shiny new technologies without fully considering how those technologies impact the customer's experience from start to finish. This oversight can lead to fragmented journeys, frustrated customers, and ultimately, a failed transformation. True digital transformation requires a customer-centric approach, focusing on streamlining and personalizing the entire customer journey across all touchpoints, both physical and digital. This means breaking down internal silos that create disjointed experiences and instead, building a cohesive omnichannel strategy that meets and exceeds ever-increasing customer expectations.
This challenge deserves its place on the list of digital transformation challenges because it strikes at the heart of why businesses undergo transformation in the first place: to better serve their customers and improve business outcomes. Features of this challenge include fragmented customer data residing in disparate systems, inconsistent experiences across different channels (website, mobile app, in-store, etc.), the difficulty in balancing personalization with data privacy concerns, legacy processes designed for internal efficiency rather than customer needs, organizational silos that prevent end-to-end journey ownership, and the constantly rising bar of customer expectations set by best-in-class experiences delivered by other companies.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Disney's MagicBand: Seamlessly integrates various aspects of the theme park experience, from park entry and hotel room access to ride reservations and payments, all through a single wearable device.
- Starbucks' Mobile App: Offers a streamlined experience for ordering, payment, and loyalty programs, making it convenient and personalized for customers.
- USAA: Designs financial services around the key life events of military members and their families, rather than focusing solely on individual products, creating a more empathetic and relevant customer experience.
Pros of Focusing on Customer Journey Integration:
- Increased Customer Loyalty and Reduced Churn: A superior customer experience fosters loyalty and reduces the likelihood of customers switching to competitors.
- Increased Cross-Sell and Upsell Opportunities: Integrated journeys provide opportunities to identify and offer relevant products or services to customers at different stages of their journey.
- Prioritization of High-Value Transformation Initiatives: A customer-centric approach helps identify which transformation projects will deliver the most value to customers and the business.
- Streamlined Processes and Technology: A journey focus can reveal and eliminate unnecessary processes and technologies.
Cons of Focusing on Customer Journey Integration:
- Cross-Functional Collaboration Challenges: Journey redesign requires collaboration across different departments, which can be difficult to achieve.
- Legacy System Limitations: Existing legacy systems may limit the ability to fully integrate customer experiences.
- Data Sophistication Requirements: Personalization requires a level of data sophistication that many organizations lack.
- High Maintenance Costs: Maintaining consistency across all touchpoints can be expensive.
Actionable Tips for Addressing Customer Journey Integration Challenges:
- Customer Journey Mapping: Conduct thorough customer journey mapping exercises with real customers to understand their needs and pain points.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): Implement CDPs to unify customer interaction data from various sources.
- Mobile-First Design: Design for mobile-first experiences that can then be extended to other channels.
- Journey Owners: Create dedicated "journey owner" roles with cross-functional authority to oversee the entire customer journey.
- Customer Effort Score (CES): Measure CES alongside traditional satisfaction metrics to understand how much effort customers are expending to interact with your business.
- Design Thinking: Employ design thinking methodologies to reimagine customer journeys from the ground up.
- Voice-of-Customer Programs: Implement voice-of-customer programs to gather continuous feedback and improve the customer experience.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
This customer-centric approach to digital transformation should be implemented from the outset of any digital transformation initiative. By prioritizing customer experience and journey integration, organizations can ensure that their efforts are aligned with customer needs and ultimately drive business success. This focus is critical for any organization seeking to thrive in today's competitive landscape, where customer expectations are higher than ever before. This is particularly pertinent for tech-savvy audiences like AI professionals, software engineers, entrepreneurs, and digital marketers who are building and interacting with digital products and services daily.
7 Key Digital Transformation Challenges Comparison
| Challenge | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legacy System Integration | High due to outdated tech and lack of APIs | Specialized legacy skills; middleware platforms | Preserves data; phased transformation; continuity | Firms with critical legacy systems | Cost-effective vs full replacement; preserves business continuity |
| Cultural Resistance to Change | Moderate; requires ongoing change management | Strong leadership; training and communication | Higher adoption rates; stronger buy-in | Organizations facing employee reluctance | Identifies concerns; improves implementation; drives buy-in |
| Data Security and Privacy Compliance | High; evolving regulations and technical controls | Security tools; compliance teams; training | Reduced breaches and penalties; enhanced trust | Data-intensive industries with regulatory need | Builds trust; regulatory alignment; competitive advantage |
| Skill Gaps and Talent Shortages | Moderate to high; continuous hiring and training | Up-skilling programs; partnerships; mentorship | Long-term capabilities; innovation | Rapid tech evolution requiring specialized talent | Builds internal digital capability; retention; fosters innovation |
| Budget Constraints and ROI Justification | Moderate; requires financial discipline and phased funding | Financial planning; business case development | Better prioritization; manageable risk | Organizations with limited funds or competing priorities | Encourages focus; risk reduction; creative funding approaches |
| Technology Selection and Architecture Decisions | High; complex multi-vendor and future-proofing | Cross-functional expertise; evaluation frameworks | Scalable, flexible architecture; competitive edge | Enterprises adopting new platforms or emerging tech | Enables agility; modularity; strategic differentiation |
| Customer Experience and Journey Integration | High; requires cross-functional collaboration | Customer research; data platforms; design teams | Improved loyalty and revenue growth | Customer-centric transformation initiatives | Drives loyalty; increases sales; identifies key customer priorities |
Turning Challenges into Opportunities
Digital transformation challenges, from legacy system integration to budget constraints, can seem like significant roadblocks on the path to innovation. This article has explored seven key obstacles that organizations commonly face: integrating outdated systems, overcoming cultural resistance, ensuring data security and privacy, addressing skill gaps and talent shortages, justifying ROI and managing budgets, making sound technology choices, and creating seamless customer journeys. Successfully navigating these hurdles is crucial for any business seeking to thrive in the digital age.
The key takeaway here is that these digital transformation challenges represent not just obstacles, but also opportunities. By proactively addressing legacy system integration, for example, you can unlock new data insights and streamline operations. Investing in training and upskilling to combat talent shortages empowers your team with valuable new capabilities. A well-defined digital transformation strategy, coupled with a clear understanding of ROI, can unlock significant budget and resource allocation.
What are your next steps? Start by assessing your organization's current digital maturity and identifying the most pressing digital transformation challenges you face. Prioritize these challenges based on their potential impact and feasibility. Develop a phased approach, starting with smaller, achievable wins to build momentum and demonstrate value. Remember to foster open communication and collaboration throughout the process to address cultural resistance and ensure buy-in across all levels.
Mastering these concepts and approaches is essential for any organization looking to leverage the power of digital technologies. Successfully navigating digital transformation challenges enables you to enhance operational efficiency, create innovative products and services, improve customer experiences, and ultimately, gain a competitive edge in today's rapidly evolving digital landscape.
The digital future is not something to be feared, but embraced. By viewing digital transformation challenges as opportunities for growth and innovation, you can position your organization for long-term success in the digital economy.