8 Data Privacy Best Practices for 2025
Enhance your data privacy strategy with these 8 data privacy best practices. Learn how to minimize risks, build trust, and stay compliant in 2025.
Protecting Your Precious Data: A Guide to Best Practices
Data breaches are costly. Lost customer trust is even worse. This listicle provides eight data privacy best practices to safeguard your data and build confidence with users. Learn how to implement core principles like Privacy by Design, data minimization, and strong access controls. We'll also cover crucial practices like data encryption, privacy impact assessments, vendor management, and employee training. Following these data privacy best practices will protect your business and solidify your reputation in 2025 and beyond.
1. Privacy by Design (PbD)
Among the most crucial data privacy best practices is Privacy by Design (PbD). This proactive approach integrates privacy considerations into every stage of the system development lifecycle, from initial design and architecture to deployment and beyond. Instead of treating privacy as an add-on or a compliance checklist item to be addressed after the fact, PbD bakes privacy directly into the specifications of technologies, operations, and information architectures. This anticipatory strategy minimizes privacy risks before they even have a chance to materialize.
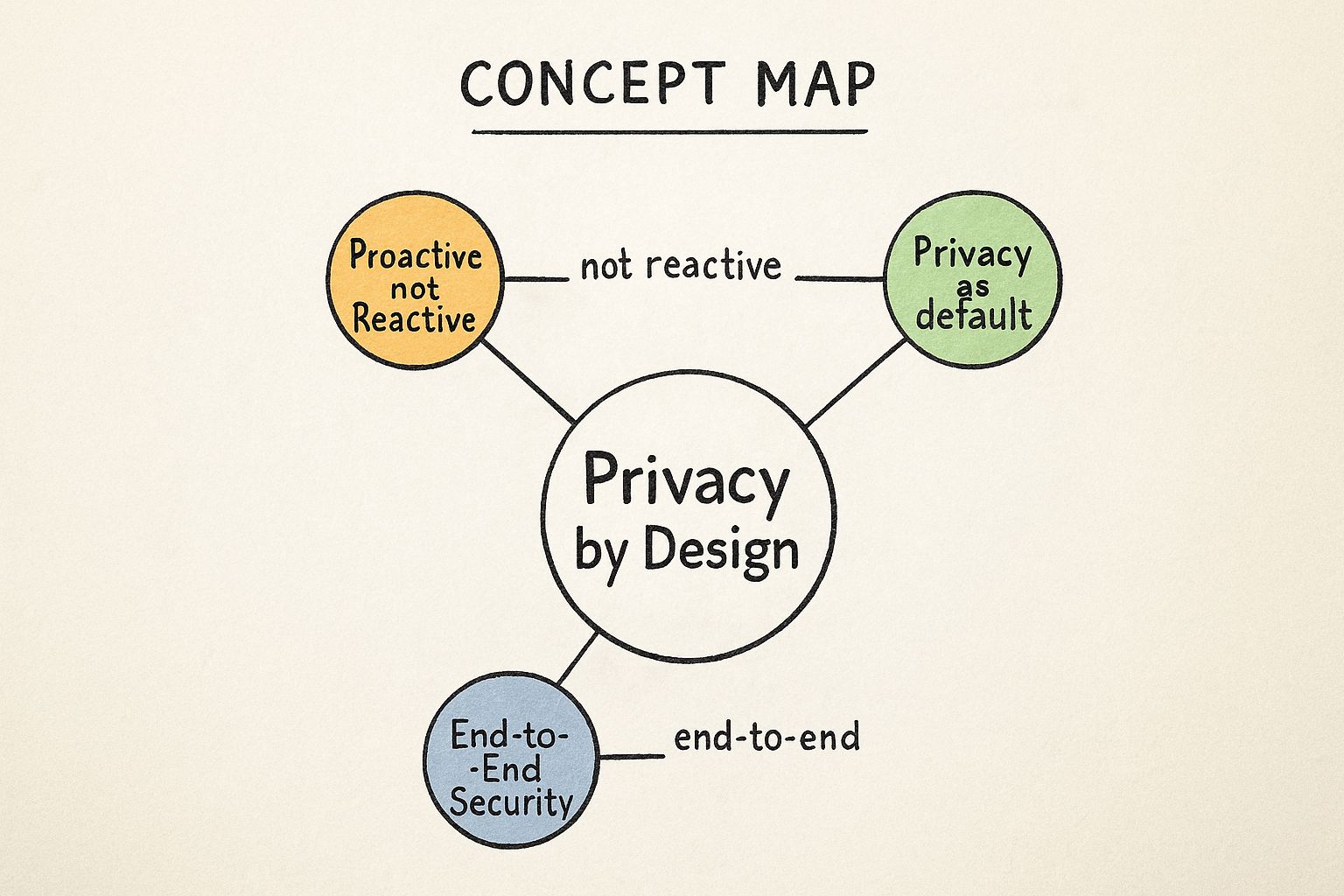
The infographic above visualizes the core components of PbD, illustrating how various concepts connect to form a comprehensive approach to data privacy. The central concept, "Privacy by Design," branches out to seven key principles: Proactive not Reactive, Preventative not Remedial, Privacy as the Default Setting, Privacy Embedded into Design, Full Functionality, End-to-End Security, and Visibility and Transparency. These principles are interconnected and mutually reinforcing. For instance, "Privacy as the Default Setting" supports "Proactive not Reactive" by ensuring privacy is automatically enabled, eliminating the need for user intervention or retroactive fixes. Similarly, "End-to-End Security" throughout the entire lifecycle strengthens "Preventative not Remedial" measures. The infographic emphasizes that PbD is not just about minimizing harm, but about creating a positive-sum environment where robust privacy enhances functionality and builds user trust.
PbD offers a multitude of features that promote robust data protection. It's proactive and preventative, embedding privacy into design from the outset. It establishes privacy as the default setting, ensuring users don't have to opt-in to be protected. PbD aims for full functionality, demonstrating that privacy doesn't have to come at the expense of usability. It champions end-to-end security throughout the data lifecycle and promotes visibility and transparency, keeping users informed about how their data is being handled. At its core, PbD respects user privacy, placing the user at the center of the design process.
Implementing PbD offers several advantages. It significantly reduces privacy risks before they become problems, minimizes the impact of potential data breaches, and fosters trust with customers and users. In the long run, PbD can even reduce compliance costs and create a competitive advantage for businesses that prioritize data protection. However, it's also important to acknowledge the potential drawbacks. Implementing PbD can require significant upfront investment and may prove challenging to integrate into existing legacy systems. It also necessitates a shift in organizational culture and can sometimes slow down initial development processes.
For AI professionals, developers, and tech-savvy entrepreneurs, incorporating PbD is particularly relevant. As AI and machine learning models become more sophisticated and data-intensive, the potential privacy implications grow exponentially. PbD provides a framework for mitigating these risks and building ethical, privacy-preserving AI systems.
Several successful examples highlight the effectiveness of PbD. Apple's App Tracking Transparency feature, requiring explicit user consent for tracking, exemplifies user-centric privacy control. Microsoft's Security Development Lifecycle integrates privacy requirements throughout the development process. Google's use of differential privacy techniques in their analytics tools demonstrates how privacy can be preserved while still enabling valuable data analysis.
Here are some actionable tips for implementing PbD:
- Conduct Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs): Start every project with a PIA to identify potential privacy risks early on.
- Create Cross-Functional Privacy Teams: Include engineers, designers, legal professionals, and other relevant stakeholders to ensure a holistic approach to privacy.
- Develop Privacy Design Patterns: Create reusable patterns for common privacy challenges to streamline development and ensure consistency.
- Integrate Privacy Requirements: Build privacy requirements directly into your development workflow.
- Provide Privacy Training: Educate all team members on privacy principles and best practices.
PbD, popularized by Dr. Ann Cavoukian and further solidified by regulations like the GDPR and standards from the ISO, deserves its place at the top of any data privacy best practices list. By proactively embedding privacy into the very fabric of systems and processes, PbD not only mitigates risks but also fosters trust, promotes innovation, and contributes to a more ethical and responsible data landscape. This approach is crucial for maintaining user trust and operating responsibly in an increasingly data-driven world, making it a cornerstone of modern data privacy best practices.
Get started with your lifetime license
Enjoy unlimited conversations with MultitaskAI and unlock the full potential of cutting-edge language models—all with a one-time lifetime license.
Demo
Free
Try the full MultitaskAI experience with all features unlocked. Perfect for testing before you buy.
- Full feature access
- All AI model integrations
- Split-screen multitasking
- File uploads and parsing
- Custom agents and prompts
- Data is not saved between sessions
Lifetime License
Most Popular€99€149
One-time purchase for unlimited access, lifetime updates, and complete data control.
- Everything in Free
- Data persistence across sessions
- MultitaskAI Cloud sync
- Cross-device synchronization
- 5 device activations
- Lifetime updates
- Self-hosting option
- Priority support
Loved by users worldwide
See what our community says about their MultitaskAI experience.
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
2. Data Minimization
Data minimization is a crucial data privacy best practice that focuses on limiting the collection and retention of personal data to only what is absolutely necessary for a specific purpose. Instead of gathering every piece of information imaginable "just in case" it might be useful later, organizations implementing data minimization identify the bare minimum data required for their operations and stick to it. This approach is fundamental to responsible data handling and forms a core component of many modern privacy regulations.

Data minimization works by implementing several key features: strictly limiting collection to necessary data points; specifying the purpose for collecting each individual data element; setting defined retention periods and limiting storage accordingly; establishing regular data purging processes to remove outdated or no longer needed information; and utilizing anonymization and de-identification techniques whenever feasible. By adhering to these principles, organizations significantly reduce their data footprint, thus minimizing potential risks and enhancing user trust.
This practice deserves a prominent place in any data privacy best practices list because it offers numerous benefits. It reduces the potential attack surface and mitigates the impact of data breaches by limiting the amount of sensitive information held. It also lowers storage and security costs, simplifies compliance with regulations like GDPR, and fosters user trust by demonstrating responsible data handling. Finally, data minimization reduces overall liability associated with data breaches and misuse.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Signal: The Signal messaging app collects significantly less metadata compared to competitors like WhatsApp, prioritizing user privacy.
- DuckDuckGo: DuckDuckGo's search engine differentiates itself by not storing personally identifiable information, offering a privacy-focused alternative to traditional search engines.
- Firefox Focus: This browser automatically deletes browsing history after each session, embodying the principle of minimizing data retention.
Pros:
- Reduced attack surface and potential breach impact
- Lower storage and security costs
- Simplified compliance with regulations (e.g., GDPR)
- Builds user trust through responsible data handling
- Reduced liability
Cons:
- May limit future data analysis opportunities
- Can be difficult to implement in big data environments
- Requires ongoing governance and monitoring
- Sometimes creates tension with business intelligence goals
Actionable Tips for Implementing Data Minimization:
- Regular Data Inventories: Conduct regular data inventories to identify and eliminate any unnecessary data collection points.
- Automated Deletion Processes: Implement automated processes for deleting data that exceeds its defined retention period.
- Data Mapping: Utilize data mapping techniques to understand data flows and identify opportunities for minimization.
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies: Consider privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) such as tokenization for necessary identifiers.
- Policy Review: Periodically review your privacy policies to ensure they accurately reflect your data minimization practices.
When and Why to Use Data Minimization:
Data minimization should be a foundational principle for any organization handling personal data, especially for AI professionals, developers, and tech-savvy entrepreneurs working with sensitive information. It’s particularly crucial when dealing with regulated data (e.g., health information, financial data) or when building applications and services that prioritize user privacy. Adopting data minimization early in the development lifecycle can significantly simplify future compliance efforts and establish a strong foundation for ethical data practices. This best practice, popularized by regulations like the EU's GDPR Article 5(1)(c), the FTC privacy framework, and the OECD Privacy Guidelines, is essential for building trust with users in today’s data-driven world.
3. Transparent Data Practices
Transparent data practices are crucial for building trust and demonstrating respect for user privacy. This core tenet of data privacy best practices involves openly communicating to users what data you collect, how you use it, who you share it with, and how long you retain it. Transparency empowers users to make informed decisions about their data and fosters a positive relationship between users and organizations. Effective transparency goes beyond simply having a privacy policy; it's about making this information accessible and understandable to everyone.
A key aspect of transparent data practices involves openly communicating your data privacy policies to users. For a good example of a transparent privacy policy, see Privacy Policy from quackr. Features of a truly transparent approach include clear, concise privacy policies, layered notices with both summaries and detailed information, and just-in-time disclosures at the point of data collection. Providing data dashboards that show users exactly what information has been collected about them further enhances transparency and control. Regularly updating users on policy changes, and explaining data usage in plain language, free of legal jargon, are also essential components. Learn more about Transparent Data Practices.
This approach offers numerous benefits. For businesses, transparency builds trust with users and customers, reducing regulatory scrutiny and compliance risks. It also differentiates brands in privacy-conscious markets and minimizes misunderstandings and complaints. For users, it empowers them to make informed choices about their data and understand how it's being handled.
However, there are some potential downsides. Transparency can expose business practices to competitors and may highlight data practices that some users find concerning. It also creates an obligation for organizations to maintain the accuracy of their disclosures and requires ongoing communication resources.
Successful examples of transparent data practices include Google's Privacy Checkup tool, which allows users to review and adjust their privacy settings, Apple's App Store privacy labels that clearly display data collection practices for each app, and Microsoft's Privacy Dashboard, giving users direct control over their data. These companies demonstrate how transparency can be integrated into product design and user experience.
To implement transparent data practices effectively, consider these tips: Use visual elements like icons and infographics to enhance understanding of complex concepts. Test your privacy notices with real users to ensure they are easily comprehended. Provide contextual notices at the moment data is collected, explaining why the information is needed. Implement a centralized privacy center where users can easily access all privacy-related information. Finally, when dealing with complex policies, use clear headings and concise summaries to make them more digestible. Following these data privacy best practices will not only improve user trust but also contribute to a more responsible and ethical data ecosystem.
4. Strong Access Controls: A Cornerstone of Data Privacy Best Practices
Strong access controls are crucial for any organization handling personal data. They form a critical layer of protection, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information, and only when necessary for legitimate business purposes. Implementing robust access controls is a foundational element of data privacy best practices and significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and misuse. This is why it's a non-negotiable for AI professionals, software engineers, tech-savvy entrepreneurs, and anyone working with sensitive data.
How Strong Access Controls Work:
The core principle behind strong access controls is the principle of least privilege. This means granting users only the minimum level of access required to perform their specific job functions. Instead of blanket permissions, access is granularly defined and tightly controlled. This approach, coupled with robust authentication mechanisms, significantly minimizes the potential for unauthorized access and data exfiltration.
Key Features of Strong Access Controls:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assigning permissions based on predefined roles (e.g., marketing, finance, administrator) simplifies management and ensures consistency.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding layers of authentication beyond passwords (e.g., security tokens, biometric verification) makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain access, even if credentials are compromised.
- Privileged Access Management: Specifically controlling and monitoring access for highly privileged accounts (e.g., system administrators) that have broad access to systems and data.
- Regular Access Reviews and Certification: Periodically reviewing and verifying user access rights helps ensure that permissions are still appropriate and removes any unnecessary access.
- Automated Account Provisioning and Deprovisioning: Streamlining the process of creating and deleting user accounts reduces administrative overhead and ensures that access is promptly revoked when an employee leaves or changes roles.
- Detailed Access Logging and Monitoring: Tracking and analyzing access activity helps identify suspicious behavior and potential breaches early on.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Healthcare: Context-aware access controls restrict access to patient records based on the user's role and the specific clinical context. For example, a nurse might only be able to access the records of patients currently under their care.
- Finance: Zero trust architectures assume no implicit trust and require verification at every access attempt, significantly strengthening security in financial institutions.
- Salesforce Shield: This platform provides field-level security and encryption, allowing organizations to control access to specific data fields within Salesforce records.
Pros of Implementing Strong Access Controls:
- Minimizes insider threat risks: Restricting access limits the potential damage a malicious or negligent insider can inflict.
- Limits the spread of breaches: Containing breaches to smaller segments of the system by restricting access.
- Creates accountability for data access: Clear audit trails show who accessed what data and when.
- Simplifies compliance audits: Demonstrating robust access controls is key for meeting regulatory requirements.
- Protects against credential-based attacks: MFA makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain access even with stolen credentials.
Cons of Implementing Strong Access Controls:
- Can create administrative overhead: Managing granular permissions requires dedicated effort.
- May slow down legitimate access in urgent situations: Strict access controls can sometimes hinder access when speed is critical.
- Requires sophisticated identity management infrastructure: Implementing and maintaining these systems can be complex.
- Can be frustrating for users if overly restrictive: Poorly designed access controls can impede productivity and create user frustration.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Implement the principle of least privilege by default. Start with minimal access and only grant additional permissions as needed.
- Require MFA for all access to systems containing personal data. This is a fundamental security best practice.
- Conduct quarterly access reviews to remove unnecessary permissions. Regular reviews keep access rights aligned with current roles and responsibilities.
- Use just-in-time access for privileged accounts. Grant elevated privileges only when needed and revoke them immediately afterward.
- Monitor and alert on unusual access patterns. Detect and respond to suspicious activity promptly.
- Automate deprovisioning when employees change roles or leave. Prevent lingering access that can pose a security risk.
Popularized By:
These best practices are promoted by leading security organizations like the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), SANS Institute, and the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA). These organizations provide valuable resources and guidance on implementing strong access controls.
By implementing strong access controls as a core element of your data privacy strategy, you create a robust defense against unauthorized access, minimize risks, and build a foundation for a strong security posture. This is especially crucial in today’s interconnected world, where protecting sensitive personal data is paramount for maintaining trust and complying with regulations.
No spam, no nonsense. Pinky promise.
5. Data Encryption: A Cornerstone of Data Privacy Best Practices
Data encryption is a fundamental pillar of any robust data privacy strategy. It's the process of transforming readable data into an unreadable, coded format (ciphertext) using a cryptographic algorithm. This coded data can only be deciphered back into its original, usable form (plaintext) with a specific decryption key. Implementing strong data encryption is crucial for anyone concerned with data privacy best practices, from individual users to large corporations. It protects sensitive information across its entire lifecycle, ensuring confidentiality even if a breach occurs.
How data encryption works is analogous to locking a valuable item in a safe. The data is the valuable item, the encryption algorithm is the safe, and the key is the combination needed to unlock it. Without the correct key, accessing the encrypted data becomes virtually impossible.
Why Encrypt Data?
Data encryption is paramount for several reasons:
- Protection against breaches: Encrypted data remains unreadable even if intercepted by malicious actors during a security breach. This significantly reduces the risk of sensitive information falling into the wrong hands.
- Compliance with regulations: Many data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, mandate data encryption as a critical security measure. Implementing encryption can help organizations achieve and maintain compliance, avoiding hefty fines and legal repercussions.
- Maintaining confidentiality: Data often travels across various networks and is stored in different locations. Encryption ensures confidentiality throughout this journey, whether the data is in transit, at rest, or in use. This is especially important when dealing with third-party services or cloud environments.
- Enabling secure collaboration: Encrypted data allows for secure multi-party computing and data sharing. Organizations can collaborate on sensitive projects without compromising data confidentiality.
Types of Data Encryption:
To effectively implement data encryption as a data privacy best practice, consider these key areas:
- Data in Transit: This protects data as it travels across networks. Transport Layer Security (TLS), especially version 1.3, is the standard for secure web communication.
- Data at Rest: This secures data stored in databases or files. Methods include full-disk encryption for endpoint devices, database and file-level encryption, and cloud providers often offer default encryption for stored data.
- Data in Use: A more challenging aspect, this involves encrypting data while it's being actively processed in memory. Homomorphic encryption is an emerging technology addressing this need, allowing computations on encrypted data without decryption.
Features and Examples:
Several technologies facilitate data encryption:
- Key management systems: Securely store and manage encryption keys, crucial for preventing data loss.
- End-to-end encryption (E2EE): Ensures only the sender and recipient can read messages, exemplified by messaging apps like WhatsApp and Signal.
- Full-disk encryption: Encrypts the entire hard drive of a device, as seen in Apple's FileVault.
- Cloud providers: Services like Google Cloud offer default encryption of data at rest.
- Financial transactions: Platforms like Venmo encrypt financial transaction data to protect sensitive user information.
Pros and Cons of Data Encryption:
While data encryption is a vital data privacy best practice, it’s crucial to be aware of both advantages and disadvantages:
Pros:
- Renders data unreadable if intercepted
- Provides a safe harbor under many breach notification laws
- Protects data across its entire lifecycle
- Maintains confidentiality across third-party environments
- Enables secure multi-party computing
Cons:
- Can impact system performance
- Key management is critical (lost keys can mean lost data)
- Implementation errors can create a false sense of security
- Some legacy systems may not support modern encryption
Actionable Tips for Implementing Data Encryption:
- Use industry-standard encryption algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA), and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) instead of creating custom solutions.
- Implement proper key management with regular rotation policies.
- Enable TLS 1.3 for all web applications and APIs.
- Consider Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) for secure key storage.
- Encrypt backups and test recovery processes.
- Document your encryption implementation for compliance purposes.
Learn more about Data Encryption to delve deeper into how API security intertwines with data encryption.
Data encryption owes much of its popularization to figures like Phil Zimmermann, creator of Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) encryption, the Electronic Frontier Foundation, and renowned cryptography expert Bruce Schneier. Their contributions highlight the importance of this essential data privacy best practice. By understanding and implementing strong encryption techniques, AI professionals, developers, entrepreneurs, and anyone handling sensitive data can significantly bolster their data privacy posture.
6. Regular Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs)
As a crucial element of data privacy best practices, regular Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) play a vital role in proactively identifying and mitigating privacy risks. For AI professionals, software engineers, tech entrepreneurs, and anyone working with personal data, understanding and implementing PIAs is essential for building trust and avoiding costly legal and reputational damage. PIAs are a structured process for evaluating the privacy implications of new or modified systems, products, or services that handle personal data, allowing you to address potential issues before they become problems.
How PIAs Work:
A PIA involves systematically analyzing how personal data is collected, used, stored, and shared within a specific project or system. This process includes:
- Systematic identification of privacy risks: Pinpointing potential vulnerabilities and threats to individual privacy.
- Evaluation of compliance with regulations: Ensuring alignment with relevant data protection laws like GDPR, CCPA, etc.
- Documentation of data flows and processing activities: Creating a clear record of how data moves through the system.
- Assessment of necessity and proportionality: Determining if the data collection and use are justified and proportionate to the purpose.
- Stakeholder consultation process: Gathering input from various teams (legal, technical, business) and potentially affected individuals.
- Recommended mitigation measures: Developing and implementing strategies to reduce identified risks.
Examples of Successful PIA Implementation:
Several organizations have successfully integrated PIAs into their workflows, demonstrating the value of this approach:
- UK National Health Service (NHS): The NHS conducts PIAs before deploying new patient data systems, ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive health information.
- Facebook: Following the FTC consent decree, Facebook implemented a more rigorous privacy review process, incorporating PIAs to address ongoing privacy concerns.
- Australian Government Agencies: PIAs are mandatory for high-risk projects involving personal data, ensuring compliance with Australian privacy legislation.
Why PIAs Deserve a Place in Data Privacy Best Practices:
PIAs are invaluable for several reasons:
- Early Risk Identification and Mitigation: Addressing privacy concerns early in the development cycle saves time and resources compared to costly redesigns after launch.
- Enhanced Compliance and Accountability: PIAs provide documented evidence of your commitment to data privacy, demonstrating due diligence to regulators.
- Reduced Risk of Legal and Reputational Damage: Proactive risk mitigation minimizes the chances of data breaches, fines, and negative publicity.
- Increased User Trust: Demonstrating a commitment to privacy through PIAs builds trust with users and strengthens your brand reputation.
Pros and Cons of PIAs:
Pros:
- Identifies and addresses risks early in development
- Creates accountability and documentation for compliance
- Reduces costly redesigns after launch
- Demonstrates due diligence to regulators
- Ensures privacy considerations are not overlooked
Cons:
- Can be resource-intensive for complex systems
- May delay project timelines
- Requires specialized privacy expertise
- Can become a checkbox exercise if not properly implemented
Actionable Tips for Implementing PIAs:
- Start Early: Integrate PIAs from the beginning of the project lifecycle.
- Use a Consistent Methodology: Develop a standardized, repeatable process for conducting PIAs.
- Involve Diverse Stakeholders: Include technical, legal, and business teams in the assessment process.
- Regular Updates: Reassess and update PIAs when significant changes occur to systems or data processing activities.
- Create Templates: Develop templates for common scenarios to streamline the process.
- Integrate Findings: Incorporate PIA findings into your overall risk management framework.
Organizations Popularizing PIAs:
- Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada
- UK Information Commissioner's Office (ICO)
- International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP)
By incorporating regular PIAs into your data privacy best practices, you can build a strong foundation for responsible data handling, minimize risks, and foster trust with your users. Whether you are developing AI models, building software applications, or launching a new online service, PIAs are a critical tool for navigating the complex landscape of data privacy.
7. Vendor Management and Third-Party Risk Assessment
In today's interconnected world, implementing robust data privacy best practices extends beyond your organization's internal walls. Number seven on our list, Vendor Management and Third-Party Risk Assessment, is crucial for maintaining control over personal data and minimizing risks associated with sharing it with external entities. This practice involves meticulously evaluating, monitoring, and managing the privacy practices of all third parties that handle your organization's personal data. It's a critical component of any comprehensive data privacy strategy, especially for AI professionals, software engineers, and tech-savvy entrepreneurs working with sensitive user information.
How it Works:
Vendor management for data privacy begins with thorough due diligence before engaging any third-party vendor. This includes scrutinizing their privacy policies, security certifications, and data handling practices. Once a vendor is selected, data processing agreements (DPAs) with strong privacy provisions should be established. These contracts should clearly outline data handling and transfer restrictions, incident response protocols, breach notification requirements, and your organization's right to audit the vendor's practices. Ongoing monitoring through regular security and privacy assessments is essential to ensure continued compliance and identify potential vulnerabilities.
Why It's Essential:
This proactive approach to vendor management offers several advantages:
- Extends privacy protection: Safeguards data even when it's outside your direct control.
- Reduces breach risks: Minimizes the likelihood of a third-party data breach impacting your organization.
- Contractual remedies: Provides legal recourse if a vendor fails to uphold their privacy obligations.
- Regulatory compliance: Helps meet legal requirements for vendor oversight, such as GDPR, CCPA, and others.
- Supply chain visibility: Identifies and addresses privacy vulnerabilities throughout your data supply chain.
Pros and Cons:
While essential, vendor management can be challenging. Here's a balanced view:
Pros:
- Enhanced data protection
- Reduced breach risks
- Contractual remedies for failures
- Regulatory compliance assistance
- Proactive vulnerability identification
Cons:
- Resource intensive, especially with numerous vendors
- Limited leverage with larger vendors
- Difficulty verifying actual practices beyond documentation
- Jurisdictional complexities with global vendors
Successful Implementations:
Several organizations have successfully implemented robust vendor management programs, often following significant data breaches that highlighted the importance of this practice. Anthem, for example, significantly enhanced their vendor management program after their 2015 data breach. Similarly, JP Morgan Chase and Microsoft have established comprehensive third-party risk management frameworks and programs (like Microsoft's Supplier Security and Privacy Assurance Program) to ensure data protection across their vendor ecosystems.
Actionable Tips:
- Categorize vendors: Classify vendors based on the sensitivity of the data they access.
- Standardized questionnaires: Utilize tools like the Standardized Information Gathering (SIG) to streamline assessments.
- Contractual requirements: Include specific privacy requirements in RFPs and contracts.
- Vendor inventory: Maintain a centralized vendor inventory with privacy risk ratings.
- Periodic reassessments: Conduct regular reassessments based on risk levels.
- Incident response playbooks: Develop specific incident response plans for vendor-related breaches.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Vendor Management and Third-Party Risk Assessment is essential anytime your organization shares personal data with external entities. This is particularly critical for businesses dealing with sensitive information, operating in regulated industries, or leveraging AI and machine learning technologies that process large datasets. This best practice deserves its place on this list due to the increasing reliance on third-party services and the escalating risks associated with data breaches. Learn more about Vendor Management and Third-Party Risk Assessment for deeper insights into this crucial aspect of data privacy.
Organizations like the Shared Assessments Program, Cloud Security Alliance, and National Association of Corporate Directors (NACD) have popularized and provided frameworks for effective third-party risk management. Implementing these best practices will significantly strengthen your data privacy posture and protect your organization from the reputational and financial damage associated with data breaches.
8. Comprehensive Employee Privacy Training
One of the most crucial data privacy best practices is comprehensive employee privacy training. Human error remains a leading cause of data breaches and privacy incidents. Therefore, a well-trained workforce acts as your first line of defense. Employee privacy training educates staff on privacy principles, organizational policies, relevant regulatory requirements (like GDPR, CCPA, etc.), and their individual responsibilities in handling and protecting sensitive personal data. This training ensures that data privacy becomes ingrained in the organizational culture, with employees understanding not just how to protect data, but also why it's so important.
How it Works:
Effective employee privacy training moves beyond simple checklists and legalese. It employs a variety of methods to engage employees and ensure comprehension:
- Role-Specific Modules: Training should be tailored to the specific responsibilities and data access levels of different employee roles. For example, customer service representatives require different training than software engineers.
- Scenario-Based Learning: Using realistic, relatable scenarios helps employees apply learned principles in practical situations. This interactive approach enhances understanding and retention.
- Regular Refresher Courses: Privacy regulations and best practices are constantly evolving. Regular refresher courses keep employees up-to-date and reinforce core concepts.
- Privacy Awareness Campaigns: Ongoing communication through newsletters, posters, and internal messaging keeps privacy top-of-mind and reinforces the organization's commitment.
- Testing and Verification: Assessing employee understanding through quizzes, simulations, or practical exercises ensures that the training is effective and identifies areas needing reinforcement.
- Incident Response Training: Employees need to know how to identify potential privacy incidents and what steps to take in case of a breach or suspected violation.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several leading organizations have demonstrated the value of robust employee privacy training:
- Deloitte: Incorporates gamified elements into their training programs, making learning more engaging and interactive.
- Intel: Utilizes a "privacy champions" network, where designated employees in each department supplement formal training and act as resources for their colleagues.
- HSBC: Has implemented mandatory data responsibility training for its entire global workforce of over 235,000 employees, highlighting the importance of privacy at scale.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Customize Training: Tailor content based on employee roles and their access to personal data.
- Microlearning: Deliver training in short, focused bursts for better knowledge retention.
- Real-World Examples: Incorporate real incidents (anonymized) as teachable moments.
- Privacy Champions: Designate privacy champions in each department to provide support and guidance.
- Interactive Elements: Use quizzes, games, and interactive scenarios to make training engaging.
- Regular Reinforcement: Send regular reminders and communications to reinforce key concepts.
Why Employee Privacy Training is Essential:
This data privacy best practice is vital for several reasons:
- Reduces Human Error: Addresses the leading cause of privacy incidents.
- Creates a Privacy-Aware Culture: Fosters a sense of responsibility and accountability among employees.
- Demonstrates Compliance: Provides evidence of your commitment to data protection regulations.
- Empowers Employees: Equips staff to identify and escalate potential privacy risks.
- Supports Privacy by Design: Helps embed privacy considerations into everyday operations.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Reduced human error, stronger privacy culture, demonstrable compliance, empowered employees, practical implementation of privacy by design.
Cons: Difficulty measuring training effectiveness, ongoing resource commitment, competition with other training priorities, potential disconnect between knowledge and behavior change without reinforcement.
Popularized By: International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP), SANS Institute, Privacy by Design Foundation.
By prioritizing comprehensive employee privacy training, organizations can significantly enhance their data protection posture, mitigate risks, and cultivate a culture of privacy. This proactive approach not only safeguards sensitive information but also builds trust with customers, partners, and employees alike.
8 Key Data Privacy Practices Comparison
| Best Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Privacy by Design (PbD) | High – requires upfront design and culture shift | Significant – cross-functional teams and training | High – reduces risks, builds trust, lowers long-term costs | New system development, product design | Proactive privacy, default protection, competitive advantage |
| Data Minimization | Medium – ongoing data inventory and retention management | Moderate – governance and monitoring efforts | Moderate – lowers breach impact, cuts costs, simplifies compliance | Data collection processes, storage practices | Limits unnecessary data, reduces liability, boosts user trust |
| Transparent Data Practices | Medium – requires clear communication and updates | Moderate – content creation and user testing | High – builds trust, reduces risks, user empowerment | User-facing privacy notices and dashboards | Clarity, user empowerment, regulatory risk reduction |
| Strong Access Controls | High – complex identity and access management | High – infrastructure for MFA, RBAC, monitoring | High – minimizes insider threats, improves audits | Sensitive data environments, regulated industries | Limits access, accountability, breach containment |
| Data Encryption | Medium to High – technical implementation and key management | Moderate to High – cryptographic infrastructure | High – data confidentiality, breach protection | Data storage, communications, cloud environments | Protects data confidentiality, supports compliance and secure computing |
| Regular Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) | Medium – process integration and expertise needed | Moderate – privacy specialists and stakeholder involvement | High – early risk detection, compliance documentation | New projects, system changes, regulatory audits | Risk mitigation, accountability, cost savings from early fixes |
| Vendor Management & Third-Party Risk Assessment | Medium to High – evaluation and ongoing oversight | High – assessments, contracts, monitoring | Moderate to High – extends privacy protection, reduces supply chain risks | Organizations with multiple vendors and partners | Controls third-party risks, supports regulatory compliance |
| Comprehensive Employee Privacy Training | Medium – curriculum development and delivery | Moderate – training resources, ongoing updates | Medium – reduces errors, promotes culture, compliance | All organizations handling personal data | Reduces human risk, fosters privacy culture, regulatory compliance proof |
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Data Privacy in the Future
In today's digital landscape, adhering to data privacy best practices is paramount. We've explored eight key strategies, from implementing Privacy by Design (PbD) and data minimization to robust access controls and regular Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs). Mastering these data privacy best practices isn't just a checklist item; it's a fundamental shift in how we approach data handling. Remember, the core principles revolve around transparency, control, and proactive risk management. This means being upfront with users about your data practices, giving them control over their information, and regularly assessing potential privacy risks.
The key takeaway here is that data privacy isn't a static concept. It's an ongoing commitment to safeguarding user information. Implementing these best practices, like encryption and vendor management, builds trust with users and mitigates potential legal and reputational risks. For developers, entrepreneurs, and marketers alike, this translates to a more sustainable and ethical business model. Think of it as future-proofing your operations in an increasingly data-sensitive world.
To truly stay ahead of the curve, consider the evolving landscape of AI and large language models. Tools like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and others offer incredible potential but also introduce new privacy considerations. When using these technologies, maintaining control over your data is crucial. Services like MultitaskAI can help by allowing you to connect to these powerful AI models using your own API keys, ensuring your sensitive data remains under your control, directly aligning with the data privacy best practices discussed.
The future of technology relies on responsible data handling. By embracing these data privacy best practices today, you are not just protecting data, you're building a foundation for a more secure and trustworthy digital future.