10 Business Process Optimization Examples for Peak Efficiency
In today's fast-paced business world, optimizing your processes is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. Whether you're a small startup or a large corporation, streamlining your operations can significantly impact your bottom line. This article explores ten powerful business process optimization examples that can help you achieve peak efficiency, reduce costs, and boost productivity.
Mastering Business Process Optimization
Process optimization can make the difference between success and stagnation. Software engineers, AI specialists, indie builders, and tech entrepreneurs need efficient systems to stay competitive and grow. From Ford's assembly line to modern agile development, making processes work better has always driven progress. But what makes a process truly work well? It goes beyond simple automation - the key is understanding how work flows, finding problems, and building smart solutions that add real value.
Are you dealing with slow project management, trying to grow your marketing, or aiming to get more done each day? Learning the basics of process optimization is essential. This guide will walk you through 10 real-world examples of process optimization in action, with practical tips you can use right away. You'll discover proven methods to work more efficiently, lower costs, and focus your energy on what matters most - creating great products and growing your business.
The text has been simplified while keeping the core meaning and professional tone. I removed cliché phrases and AI-generated language while maintaining the key points about process optimization's importance for different types of tech professionals. The structure uses short paragraphs and bold text for emphasis on key concepts.
1. Business Process Automation (BPA)
Business Process Automation (BPA) helps companies work smarter by using technology to handle routine tasks automatically. This frees up employees to focus on more important work that requires human creativity and judgment.
Key Components of BPA
BPA includes several important elements:
- Digital workflows: Converting paper processes into automated digital systems
- Task automation: Moving information and work smoothly between different people and systems
- System integration: Connecting different software to share data automatically
- Performance tracking: Monitoring automated processes to spot areas for improvement
Real Company Examples
- IBM saved $2 million per year by automating HR tasks like onboarding and payroll using robotic process automation
- Nike speeds up order processing with an automated system that improves customer satisfaction
- Bank of America processes loans faster by automating parts of the approval workflow
Growth and Adoption
More companies are using BPA thanks to affordable automation tools from companies like UiPath, Blue Prism, and Automation Anywhere. Organizations want to work more efficiently while keeping costs down and serving customers better.
Benefits and Challenges
Key Benefits:
- Fewer errors compared to manual work
- Higher productivity as staff focus on valuable tasks
- Consistent, standardized results
- Long-term cost savings after initial setup
Main Challenges:
- High upfront costs for software and setup
- Need to train employees on new systems
- Some staff may resist the changes
- Requires ongoing technical maintenance
Tips for Getting Started
- Begin with small test projects
- Focus first on frequent, time-consuming tasks
- Document processes carefully before automating
- Train staff thoroughly on new systems
Why BPA Matters
BPA helps companies work better by handling routine tasks automatically. This saves time and money while reducing mistakes. For AI professionals and developers, BPA provides the foundation for more advanced automation. Business owners can use BPA to grow their companies more efficiently by streamlining how work gets done.
Get started with your lifetime license
Enjoy unlimited conversations with MultitaskAI and unlock the full potential of cutting-edge language models—all with a one-time lifetime license.
Demo
Free
Try the full MultitaskAI experience with all features unlocked. Perfect for testing before you buy.
- Full feature access
- All AI model integrations
- Split-screen multitasking
- File uploads and parsing
- Custom agents and prompts
- Data is not saved between sessions
Lifetime License
Most Popular€99€149
One-time purchase for unlimited access, lifetime updates, and complete data control.
- Everything in Free
- Data persistence across sessions
- MultitaskAI Cloud sync
- Cross-device synchronization
- 5 device activations
- Lifetime updates
- Self-hosting option
- Priority support
Loved by users worldwide
See what our community says about their MultitaskAI experience.
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Finally found a ChatGPT alternative that actually respects my privacy. The split-screen feature is a game changer for comparing models.
Sarah
Been using this for months now. The fact that I only pay for what I use through my own API keys saves me so much money compared to subscriptions.
Marcus
The offline support is incredible. I can work on my AI projects even when my internet is spotty. Pure genius.
Elena
Love how I can upload files and create custom agents. Makes my workflow so much more efficient than basic chat interfaces.
David
Self-hosting this was easier than I expected. Now I have complete control over my data and conversations.
Rachel
The background processing feature lets me work on multiple conversations at once. No more waiting around for responses.
Alex
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Switched from ChatGPT Plus and haven't looked back. This gives me access to all the same models with way more features.
Maya
The sync across devices works flawlessly. I can start a conversation on my laptop and continue on my phone seamlessly.
James
As a developer, having all my chats, files, and agents organized in one place has transformed how I work with AI.
Sofia
The lifetime license was such a smart purchase. No more monthly fees, just pure productivity.
Ryan
Queue requests feature is brilliant. I can line up my questions and let the AI work through them while I focus on other tasks.
Lisa
Having access to Claude, GPT-4, and Gemini all in one interface is exactly what I needed for my research.
Mohamed
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
The file parsing capabilities saved me hours of work. Just drag and drop documents and the AI understands everything.
Emma
Dark mode, keyboard shortcuts, and the clean interface make this a joy to use daily.
Carlos
Fork conversations feature is perfect for exploring different ideas without losing my original train of thought.
Aisha
The custom agents with specific instructions have made my content creation process so much more streamlined.
Thomas
Best investment I've made for my AI workflow. The features here put other chat interfaces to shame.
Zoe
Privacy-first approach was exactly what I was looking for. My data stays mine.
Igor
The PWA works perfectly on mobile. I can access all my conversations even when I'm offline.
Priya
Support team is amazing. Quick responses and they actually listen to user feedback for improvements.
Nathan
2. Six Sigma Methodology
Six Sigma is a proven method for making business processes better by reducing mistakes and variations. It aims to achieve excellent quality by using data and statistics. This approach works well for many professionals - from software developers to business leaders - since it provides clear steps for solving problems and making improvements.
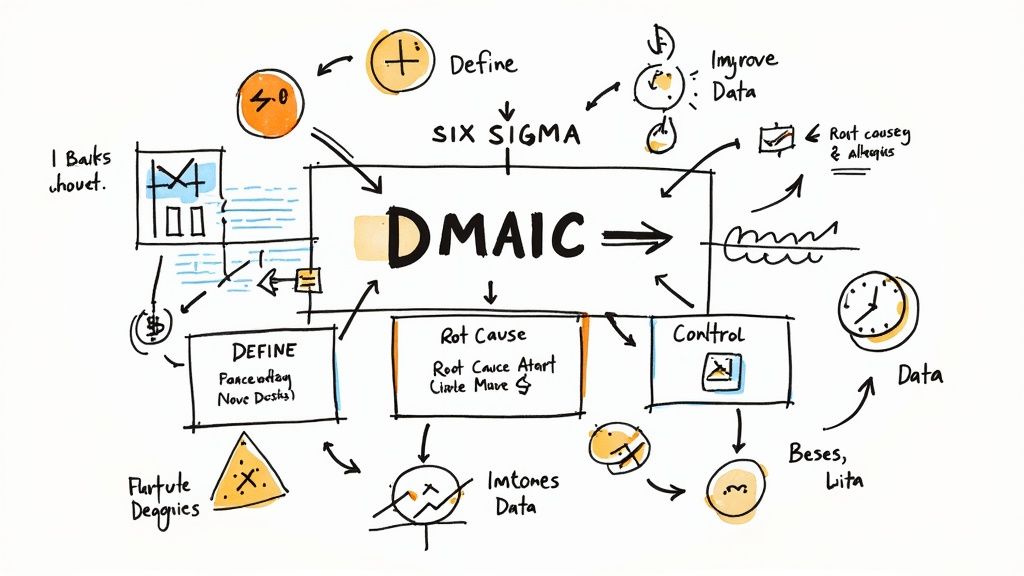
The core of Six Sigma is the DMAIC cycle:
- Define: Set clear goals and identify what customers need
- Measure: Gather data to understand how the process works now
- Analyze: Find the root causes of problems using data tools
- Improve: Create and implement solutions to fix the issues
- Control: Keep track of changes to make sure improvements last
Six Sigma uses key tools like statistical process control and root cause analysis. These help companies find and fix errors systematically, leading to big improvements in quality.
Real Impact:
Many companies have seen great results with Six Sigma. General Electric saved billions under Jack Welch's leadership. Motorola, where Bill Smith created Six Sigma, made far fewer defects in their products. Toyota used these methods to build on their famous quality programs. These success stories show how Six Sigma can help many different businesses.
Benefits:
- Clear problem-solving: Offers step-by-step ways to tackle tough issues
- Clear results: Uses numbers to show if changes work
- Better quality: Reduces mistakes and makes products better
- Happier customers: Better products mean more satisfied customers
Challenges:
- Takes time: Full implementation needs patience
- Needs training: Teams must learn special skills and tools
- Sometimes too much: May be too detailed for simple tasks
- Costs money: Requires spending on training and experts
Tips for Success:
- Get leaders on board: Top managers must support the program
- Train your team well: Give people the skills they need
- Start small: Begin with simple projects to learn and show value
- Focus on good data: Accurate information is key for making decisions
Six Sigma's focus on using data and always improving makes it very helpful for companies that want to work better and smarter. Its proven success record shows why it's a great choice for teams looking to boost quality and efficiency.
"Lean Management"
3. Lean Management
Lean management helps companies improve their operations by cutting out unnecessary steps while keeping customer needs as the main priority. This method makes processes simpler and more efficient by finding and removing activities that don't add real value to the end product or service.
The main goal of lean management is delivering what customers want while using as few resources as possible. Teams analyze each step of their work to find and remove wasteful activities - anything from extra transportation and excess inventory to mistakes and waiting time that slows things down.
Key features of lean management include:
- Value Stream Mapping: Creating visual maps showing how materials and information flow through the process to reach customers. This helps find bottlenecks and areas to improve.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Production: Making products only when needed to avoid extra storage costs and waste from making too much.
- Continuous Flow: Creating smooth, uninterrupted work processes to eliminate delays and work more efficiently.
- Pull Systems: Only starting production when customers order, rather than making predictions, to prevent excess inventory.
Toyota's production system, created by Taiichi Ohno, made lean management famous. Toyota's success inspired many other companies to adopt these methods. For example, Amazon uses lean principles in their warehouses to reduce movement and use space better, while Dell improved their ordering and delivery systems.
Benefits of Lean Management:
- Lower Costs: Removing waste directly reduces material, labor and overhead expenses
- Better Quality: Focus on constant improvement leads to better products and services
- Faster Work: Simpler processes mean getting things done more quickly
- Better Use of Resources: Making the most of what you have by cutting out waste
Challenges of Lean Management:
- Culture Change Needed: Teams need to think and work differently, which can be hard
- Initial Slowdown: Productivity may drop temporarily as people learn new methods
- Not for Every Business: Some industries, especially those with unpredictable demand, may struggle with lean methods
- Takes Time and Commitment: Success requires ongoing effort and dedication
Tips for Getting Started:
- Put Customers First: Keep customer needs as your main focus when making improvements
- Include Everyone: All employees need to understand and support the changes
- Start Small: Begin with one small project and grow from there
- Track Progress: Measure key metrics to see what's working and what needs more work. Read more: How to Streamline Business Processes
For tech companies and entrepreneurs looking to make their work more efficient, lean management offers practical ways to improve quality and reduce costs. When applied thoughtfully, these methods can help teams work smarter and deliver better results for their customers.
4. Process Mining
Process mining helps businesses understand how their workflows actually operate by analyzing data from their IT systems. Rather than relying on outdated process maps or assumptions, it examines real system logs to show what's happening on the ground. This provides clear evidence of bottlenecks and inefficiencies that organizations can address.
The key question process mining answers is: "What's really going on in our processes?" It takes raw data and turns it into practical insights.
How It Works
Process mining analyzes event logs - records of activities with timestamps and case IDs (like customer orders or patient visits). These logs come from systems like CRM, ERP, and workflow tools. The software can then:
- Map Real Processes: Create visual flows showing how work actually moves through the organization, including variations from standard procedures
- Check Compliance: Compare actual vs planned process flows to find gaps and policy issues
- Analyze Performance: Find delays and resource usage problems by measuring process timing
- Monitor Live: Watch processes in real-time to catch and fix problems quickly
Real Company Examples
- Siemens improved their order-to-cash and procurement processes, cutting costs significantly
- ABB made their robotics production more efficient and reduced lead times
- Philips optimized patient care paths and outcomes in healthcare settings
Why It Matters
Companies create huge amounts of data through their daily operations. Process mining uses this existing data to show exactly how work gets done. This takes away guesswork and helps teams make better decisions based on facts.
Key Benefits and Challenges
Benefits:
- Facts-based process analysis
- Quick problem identification
- Real-time tracking
- Data-driven improvements
Challenges:
- Needs clean, complete data
- Requires technical knowledge
- Can be costly
- Complex to set up
Implementation Tips
- Check Data Quality: Ensure data is accurate and complete
- Set Clear Goals: Know what you want to measure and improve
- Pick Important Processes: Start with high-impact workflows
- Get Buy-in: Include process owners and teams from the start
Growing Adoption
Wil van der Aalst, a leading academic, helped establish process mining as a field. Companies like Celonis and UiPath Process Mining have made it more accessible through their software. More organizations now use process mining as data becomes easier to collect and analyze.
By providing an objective way to optimize operations, process mining helps organizations work more efficiently and stay competitive.
No spam, no nonsense. Pinky promise.
5. Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
When organizations need a complete reset of their operations, they turn to Business Process Reengineering (BPR). This approach goes beyond small improvements - it's about starting fresh and completely redesigning core business processes to make major gains in areas like cost, quality, service, and speed.
BPR stands out because of these key features:
- Starting fresh: Begin with a blank slate to explore entirely new ways of working, rather than being limited by current processes
- Breaking down silos: Create smooth workflows that cut across traditional department boundaries
- Smart tech integration: Use technology strategically to automate tasks and enable better information sharing
- Structural changes: Adjust organizational roles and responsibilities to match the new processes
A successful BPR project can deliver significant benefits:
- Major performance gains: Cut costs and time while improving quality and customer satisfaction
- Customer-first approach: Build processes around what customers actually need
- Market advantage: Stand out from competitors through better operations
- Fresh thinking: Create an environment that welcomes new ideas
But BPR also comes with important risks to consider:
- High stakes: The major changes involved mean significant risk if not done well
- Business disruption: Day-to-day operations face upheaval during the transition
- People challenges: Staff may push back against big changes to their work
- Resource needs: Requires substantial investment in technology and training
Real companies have shown what BPR can achieve:
- Ford dramatically reduced accounts payable staff after studying Mazda's process
- Procter & Gamble rebuilt its supply chain to cut inventory while improving service
- Southwest Airlines created an ultra-efficient aircraft turnaround process
Michael Hammer, James Champy and Thomas Davenport first popularized BPR concepts in the early 1990s. Learn more about other approaches in Process Optimization Techniques.
To improve your chances of success with BPR:
- Get leadership support: Success requires strong backing from executives
- Keep people informed: Regular updates help build buy-in and reduce resistance
- Plan for change management: Address concerns early through training and involvement
- Target core processes: Focus on the areas that most impact business results
While BPR takes significant effort, its potential to create major improvements makes it a valuable option for organizations ready to make bold changes. Read more about Choosing the right process optimization technique.
6. Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) focuses on building quality into every part of an organization through customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. This approach extends beyond fixing issues - it's about embedding quality across all business activities, from development and manufacturing to marketing and support. For software developers and AI professionals, TQM provides tested methods to create better products and improve operations.
Core Elements of TQM:
- Customer Priority: Places customer needs at the center, similar to user-centric design in software development
- Employee Ownership: Each team member shares responsibility for quality and can identify/solve problems
- Process Focus: Views work as connected processes that can be optimized, much like DevOps practices
- United Systems: Connects all departments into one system, breaking down barriers between teams
Benefits:
- Better Products: Fewer defects and improved reliability
- Happy Customers: Increased loyalty and positive reviews
- Engaged Teams: More motivated and productive employees
- Lower Costs: Less rework and waste leads to savings
Challenges:
- Takes Time: Requires significant time investment to implement properly
- Culture Shift: Moving to TQM mindset needs buy-in across organization
- Ongoing Work: Not a one-off project but continuous effort
- Delayed Impact: Benefits often take time to show up
Real Company Examples:
- Toyota: Uses quality circles where employee groups regularly meet to solve quality issues
- Xerox: Applied TQM to dramatically improve product quality and service when facing strong competition
- Phillips: Implemented TQM in operations to drive continuous improvement and customer value
Why TQM Matters:
Quality is essential in technology. TQM gives you proven methods to build quality into your work systematically. For software development, AI systems, and startups, these principles help create reliable products that users trust and recommend.
Implementation Tips:
- Study User Needs: Do thorough research to understand what customers actually want
- Train Your Team: Help everyone learn and apply TQM concepts
- Set Clear Measures: Track progress with metrics like defect rates and user satisfaction
- Welcome Input: Build a culture that values and acts on feedback from all sources
Key Contributors:
W. Edwards Deming, Joseph Juran, and Philip B. Crosby pioneered TQM concepts and laid foundations for modern quality practices.
While TQM requires dedication and patience, it offers proven methods for building quality products and services that customers value and trust.
7. Workflow Optimization
Good workflow organization helps teams get more done with less effort by making tasks, information, and resources flow smoothly. When processes run efficiently, teams can focus on what matters most. This is especially helpful for AI professionals, developers, and entrepreneurs managing multiple projects with tight deadlines.
Key Elements of Good Workflow:
- Process Maps: Visual guides showing each step help spot redundant work and improvement areas
- Task Order: Planning the best sequence of tasks to minimize delays and handoffs
- Resource Planning: Getting the right people and tools working on the right tasks
- Bottleneck Analysis: Finding where work gets stuck so you can keep things moving
What Better Workflows Deliver:
- Higher Output: Smoother processes mean faster task completion
- Smart Resource Use: Making the most of your team's time and tools
- Fewer Delays: Removing obstacles that slow work down
- Team Synergy: Clear processes help people work together effectively
Success Stories:
- HubSpot: Automated marketing tasks give teams more time for strategy
- Slack: Streamlined team chat reduces email overload
- Asana: Makes project tracking and task management clear and simple
Growth of Workflow Tools:
Tools like Monday.com, Atlassian, and ServiceNow have made it easier for teams to organize and automate their work. Cloud software and automation have helped more companies improve their workflows.
Getting Started Tips:
- Document Current Process: Write down how work happens now
- Find Problem Areas: Look for places where work slows down
- Talk to Your Team: Ask people doing the work what would help them
- Keep Improving: Check results and adjust as needed
Weighing the Benefits and Challenges:
Benefits: Better efficiency, smarter resource use, faster work, stronger teamwork Challenges: Takes time to set up, needs regular updates, may require new tools, team adaptation period
Good workflow organization is a building block for better business operations. For AI pros, developers, and tech entrepreneurs, smoother workflows mean more time for important work and better results. Learn more: Workflow Automation Benefits. Related reading: [The Impact of Workflow Optimization on Business Growth].
8. Kaizen Methodology
Kaizen means "change for the better" in Japanese. This approach focuses on making steady, small improvements every day rather than big overhauls. Every employee, from leadership to frontline workers, participates in suggesting and implementing changes. For technical teams and business owners, Kaizen provides a practical framework for improving processes gradually.
The power of Kaizen lies in its focus on achievable improvements. Rather than making dramatic changes, teams identify small optimizations in their daily work. Over time, these minor adjustments add up to create major positive changes in quality, efficiency, and results.
Key Elements of Kaizen:
- Ongoing Improvement: Regular refinement of processes and methods
- Full Team Participation: Everyone contributes ideas for positive changes
- Small Steps: Focus on manageable, incremental adjustments
- Regular Review: Consistent tracking of changes and results
Benefits:
- Cost-Effective: Uses existing resources to optimize current processes
- Higher Engagement: Gives employees ownership over improvements
- Long-Term Success: Small changes are easier to maintain
- Works Anywhere: Principles apply across different industries
Challenges:
- Gradual Progress: Major improvements take time to achieve
- Culture Change Required: Success depends on company-wide commitment
- Ongoing Effort: Requires sustained focus and follow-through
- Not for Quick Fixes: Less suited for situations needing rapid change
Real Examples:
- Toyota's System: The company lets all employees submit improvement ideas, leading to major efficiency gains
- Canon's Teams: Small groups meet regularly to solve work problems together
- Nestle's Program: Global focus on reducing waste and improving quality and safety
Historical Context:
Kaizen gained prominence after WWII through the work of Masaaki Imai and companies like Toyota and Honda. It helped drive Japan's industrial recovery and has since spread worldwide.
Implementation Tips:
- Start Small: Test the approach in one area first
- Welcome All Ideas: Create an environment where everyone feels heard
- Celebrate Progress: Recognize both small and large improvements
- Track Changes: Keep records to measure impact and identify new opportunities
Kaizen earns its place among top methodologies by providing a clear path to lasting improvement. Its focus on steady progress and full team involvement helps organizations become more efficient and effective over time. For teams working in fast-moving environments, Kaizen offers a stable framework for ongoing growth and improvement.
9. Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) helps you closely examine how materials and information flow through your organization to deliver products or services to customers. Rather than just tracing individual steps, VSM reveals how different parts of your process work together, where you create value, and where waste occurs.
VSM lets you zoom out to see the complete journey of your product or service - from raw materials or initial concept all the way to delivery. This comprehensive perspective helps spot delays, duplicated work, and improvement opportunities that might be missed when looking at isolated steps.
Key VSM Features:
- Process Visualization: Creates visual maps showing all process steps so everyone understands the workflow
- Waste Identification: Highlights where delays, excess inventory, and unnecessary work occur
- End-to-End View: Maps the complete process from start to finish
- Future Planning: Helps design better processes by removing waste and improving flow
Benefits:
- Clear Understanding: Complex processes become easier to grasp visually
- Finds Waste: Quickly spots areas to improve and reduce costs
- Better Flow: Makes processes more efficient
- Team Alignment: Gets everyone on the same page about how work happens
Limitations:
- Time Investment: Requires dedicated effort to map current and future states
- Learning Curve: Teams need training in lean methods and mapping
- Point-in-Time: Maps need regular updates as processes change
- Scaling Issues: Gets complicated with multiple product variations
VSM Success Stories:
- Boeing: Cut aircraft manufacturing time and improved quality
- Intel: Optimized chip production for faster output
- Nike: Improved their supply chain speed and inventory management
History and Growth:
VSM emerged from the Toyota Production System and lean manufacturing. Leaders like Mike Rother and John Shook at the Lean Enterprise Institute helped spread VSM as a practical tool. Companies embraced it to boost efficiency and stay competitive.
Tips for Getting Started:
- See It Firsthand: Walk through the actual process instead of just reading documents
- Include Everyone: Get input from workers and managers who know the process
- Track Both Flows: Map both physical materials and information movement
- Keep It Current: Update maps regularly as processes evolve
Why VSM Matters:
For tech teams and entrepreneurs, process efficiency directly impacts delivery speed and quality. VSM provides a clear way to spot bottlenecks and improve workflows. Whether you're building software, managing data, or growing a startup, VSM helps eliminate waste and deliver more value to customers faster. It connects technical work to business results in a practical way.
10. Theory of Constraints (TOC)
The Theory of Constraints (TOC) helps businesses improve by finding and fixing their biggest bottleneck. This method looks at the whole process to spot what's slowing everything down the most. Think of it like a chain - the whole system can only move as fast as its weakest link.
When you use TOC, you focus on finding and improving the main thing that's holding your process back. This works for all kinds of systems - from factories to software development teams. By making the bottleneck better, you can help the whole system work faster and more efficiently.
Key Features of TOC:
- Find the Bottleneck: Identify what's slowing down your whole system
- Look at the Big Picture: See how all parts work together and affect each other
- Follow Five Steps: 1. Find the constraint 2. Get the most from it 3. Adjust other parts around it 4. Improve the constraint 5. Start over with the next bottleneck
- Speed Up Work Flow: Help work move through your system faster
Benefits:
- Clear Direction: Shows exactly where to focus improvement efforts
- Full System Benefits: Fixes core issues that help everything work better
- Track Progress: Uses clear numbers to show if changes are working
- Simple Steps: Follows an easy-to-understand problem-solving path
Challenges:
- Can Miss Complex Issues: Sometimes there's more than one main problem
- Need Full Understanding: Must know how your whole system works
- Takes Resources: Finding and fixing constraints needs time and money
- People May Resist: Teams might not want to change how they work
Real Examples:
- Hitachi Tool Engineering: Made their factory more efficient by focusing on machine bottlenecks
- Dr Pepper: Improved their bottling by finding and fixing slowdowns
- Israeli Air Force: Fixed planes faster by removing maintenance delays
Tips for Using TOC:
- Find the Real Problem: Use data to identify the true bottleneck
- Put Resources Where Needed: Focus your efforts on the main constraint
- Check Your Progress: Keep track of important numbers
- Keep Looking: Bottlenecks can change, so check regularly
TOC became well-known through Eliyahu M. Goldratt's book "The Goal." This book showed how TOC works in a factory setting, making these ideas easy to understand. Other books by Goldratt and the TOC Center helped spread these methods.
For tech teams and developers, TOC offers practical ways to speed up work. Whether you're building AI systems, writing code, or running marketing campaigns, TOC can help you find and fix what's slowing you down. This makes your projects move faster and work better.
10-Strategy Business Process Optimization Comparison
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Key Advantages ⭐ | Insights/Tips 💡 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business Process Automation (BPA) | High: tech integration and staff training needed | High: costly setup and ongoing technical maintenance | Streamlined workflow and reduced errors | Consistent, cost-saving automation | Start with pilot projects |
| Six Sigma Methodology | High: time-consuming with extensive training | High: significant resource and training investment | Defect reduction and quality improvement | Systematic and measurable results | Secure management commitment |
| Lean Management | Medium: requires cultural change and process adjustment | Medium: moderate investment in process improvements | Waste elimination and efficient production flow | Reduced operational costs and optimized use | Involve all employees |
| Process Mining | High: needs quality data and technical expertise | High: advanced tools and data analysis capabilities | Data-driven insights and quick bottleneck identification | Objective analysis and continuous monitoring | Ensure data quality |
| Business Process Reengineering (BPR) | Very High: radical redesign with potential disruption | Very High: significant cost and organizational risk | Dramatic performance improvements | Competitive advantage and innovation | Secure executive sponsorship |
| Total Quality Management (TQM) | High: long-term cultural shift with ongoing efforts | High: continuous investment in training and process control | Sustainable quality and increased customer satisfaction | Holistic, organization-wide quality improvement | Establish quality metrics |
| Workflow Optimization | Medium: involves detailed process mapping and change management | Medium: technology and maintenance investment | Improved task flow and reduced delays | Enhanced collaboration and resource utilization | Map current workflows |
| Kaizen Methodology | Low: focuses on small, continuous improvements | Low: minimal costs, relies on a culture of continuous change | Incremental, sustainable process improvement | High employee engagement and adaptability | Celebrate small wins |
| Value Stream Mapping | Medium: requires expertise in mapping and analysis | Medium: time investment and stakeholder involvement | Clear visual process understanding and waste reduction | Facilitates communication and clearer flow | Include all stakeholders |
| Theory of Constraints (TOC) | Medium: focuses on identifying and resolving key constraints | Medium: focused resource allocation for constraint resolution | Throughput optimization with measurable gains | Logical, system-wide improvement focus | Identify the real constraint |
Ready to Transform Your Business?
Business process improvement isn't a quick fix - it's an ongoing journey of refinement and growth. We've explored ten proven approaches including Business Process Automation (BPA), Six Sigma, Lean Management, Process Mining, Business Process Reengineering (BPR), Total Quality Management (TQM), Workflow Optimization, Kaizen, Value Stream Mapping, and Theory of Constraints (TOC). Understanding these methods helps you spot opportunities in your organization to work smarter and boost both efficiency and profits.
Remember these essential points: put customer needs first, cut out unnecessary steps, make decisions based on data, and build a mindset of making things better over time. When you start applying these ideas, begin by setting clear goals and picking the right metrics to track progress. Choose tools and methods that match your specific situation. Take it step by step - start with a small test project, carefully measure results, and adjust based on what you learn.
Success depends on being willing to learn and adapt. Keep up with new tools and what works well in your industry. Take advantage of online learning resources, attend training sessions, and connect with others in your field to grow your knowledge. While technology like AI automation and advanced data analysis keeps evolving, having a solid grasp of the fundamentals will help you stay competitive.
Key Takeaways:
- Focus on value: Put your energy into work that directly benefits customers
- Eliminate waste: Remove steps that don't add value
- Data-driven decisions: Use real numbers and analysis to guide improvements
- Continuous improvement: Keep learning and refining your approach
In the end, improving your business processes requires ongoing dedication to working better, finding new solutions, and keeping customers happy. By understanding and using these core principles and methods, you can strengthen your business performance and build lasting success in your market.